Introduction to Skin Grafting
Skin grafting has transformed the landscape of medical and cosmetic surgery by allowing individuals with severe skin injuries or defects to heal and regain both function and appearance. This surgical procedure transfers healthy skin from a donor site to a damaged area, promoting healing and reducing the risk of complications. Skin grafting has become essential in treating burns, traumatic wounds, and various skin disorders, offering patients a chance for recovery with minimal scarring.
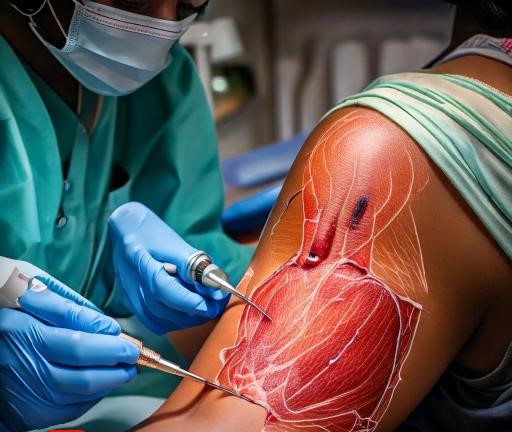
What is Skin Grafting?
Skin grafting involves transplanting skin tissue from one part of the body to another, aiming to restore skin integrity in damaged areas. This technique is widely used in plastic and reconstructive surgery, enhancing both functional and aesthetic outcomes for patients.
Brief History of Skin Grafting
Skin grafting has a rich history, dating back to ancient civilizations where rudimentary methods were used to treat wounds. Over centuries, the technique evolved, with major advancements in the 19th and 20th centuries making it a reliable option for severe injuries. Today, skin grafting is a critical component of modern surgical care.
Importance in Modern Medicine
Modern medicine relies on skin grafting for diverse applications—from treating severe burns to complex reconstructive surgeries. By providing durable, life-enhancing solutions, skin grafts have become indispensable in plastic surgery, trauma care, and beyond.
Types of Skin Grafts
Split-Thickness Grafts
This common type of graft includes the epidermis and part of the dermis. It’s primarily used for large wounds and heals relatively quickly.
Full-Thickness Grafts
These grafts contain both the epidermis and entire dermis, providing better durability and a more natural appearance, often used for smaller but highly visible areas like the face.
Composite Grafts
A composite graft involves layers of skin and other tissues, such as cartilage, suitable for reconstructing complex areas that require both skin and structural support.
Reasons for Skin Grafting
Burns and Wounds
Skin grafting is essential for healing extensive burns or traumatic wounds, reducing the risk of infection, and promoting quicker recovery.
Cosmetic Reconstructive Surgery
For patients seeking reconstructive surgery due to congenital defects or scars, skin grafting enhances appearance and functionality.
Skin Diseases and Disorders
Grafting is used to treat skin diseases that result in tissue loss, providing a viable treatment option for conditions that cause significant skin damage.
Preparing for a Skin Graft
Medical Evaluation
A thorough evaluation by a qualified surgeon is crucial to assess the patient’s overall health and determine graft suitability.
Pre-Surgery Instructions
Patients are advised on pre-surgery protocols, which may include adjustments in medication, diet, and hygiene.
Establishing Expectations
Setting realistic expectations about the recovery process and potential outcomes helps patients mentally prepare for the procedure.
The Surgical Process
Donor Site Selection
The donor site is carefully selected based on the required type and size of the graft.
Removal and Transfer Techniques
The graft is meticulously harvested using advanced tools to ensure minimal damage to both donor and receptor sites.
Applying the Graft to Receptor Site
Once harvested, the graft is positioned on the receptor site and carefully secured for optimal adherence and healing.
Post-Surgery Care
Immediate Aftercare Needs
Proper wound care, dressing changes, and medication management are essential for preventing infection and supporting graft healing.
Potential Complications
Complications such as infection, graft rejection, or scarring are monitored closely. Patients are informed about signs to watch for in recovery.
Long-Term Care and Monitoring
Regular follow-up appointments help track the graft’s integration and overall healing, allowing for timely intervention if complications arise.
Recovery and Healing
Timeline for Healing
Healing typically progresses over several weeks to months, with most patients achieving significant improvement within three to four weeks.
Physical and Emotional Impact
Recovering from skin graft surgery can be challenging, requiring both physical resilience and mental support to cope with the healing process.
Tips for Faster Recovery
Key practices include adhering to follow-up care, avoiding stress on grafted areas, maintaining a healthy diet, and staying hydrated to support skin regeneration.
Recent Advancements in Skin Grafting
Improved Harvesting Techniques
Minimally invasive harvesting techniques reduce scarring and enhance the survival rate of grafts.
Innovations in Graft Preservation
Advances in graft preservation methods improve success rates by maintaining optimal cell vitality during transplantation.
Future of Skin Grafting Technology
Emerging technologies, such as 3D bioprinting and stem cell applications, hold promising potential for custom-made grafts with improved integration and reduced rejection risk.
Stories of Success
Patient Testimonials
Patients often report renewed confidence and quality of life post-surgery, especially those recovering from trauma and burns.
Case Studies
Various cases show how skin grafting provides effective solutions for complex injuries, offering insights into recovery timelines, complications, and outcomes.
Conclusion
Skin grafting is a powerful tool in modern medicine, offering numerous benefits for patients dealing with severe skin injuries and disorders. By consulting a skilled surgeon, patients can gain a better understanding of their options and what to expect from skin grafting procedures. As advancements continue, the future of skin grafting looks promising, providing quicker recovery and better outcomes for countless individuals in need.
