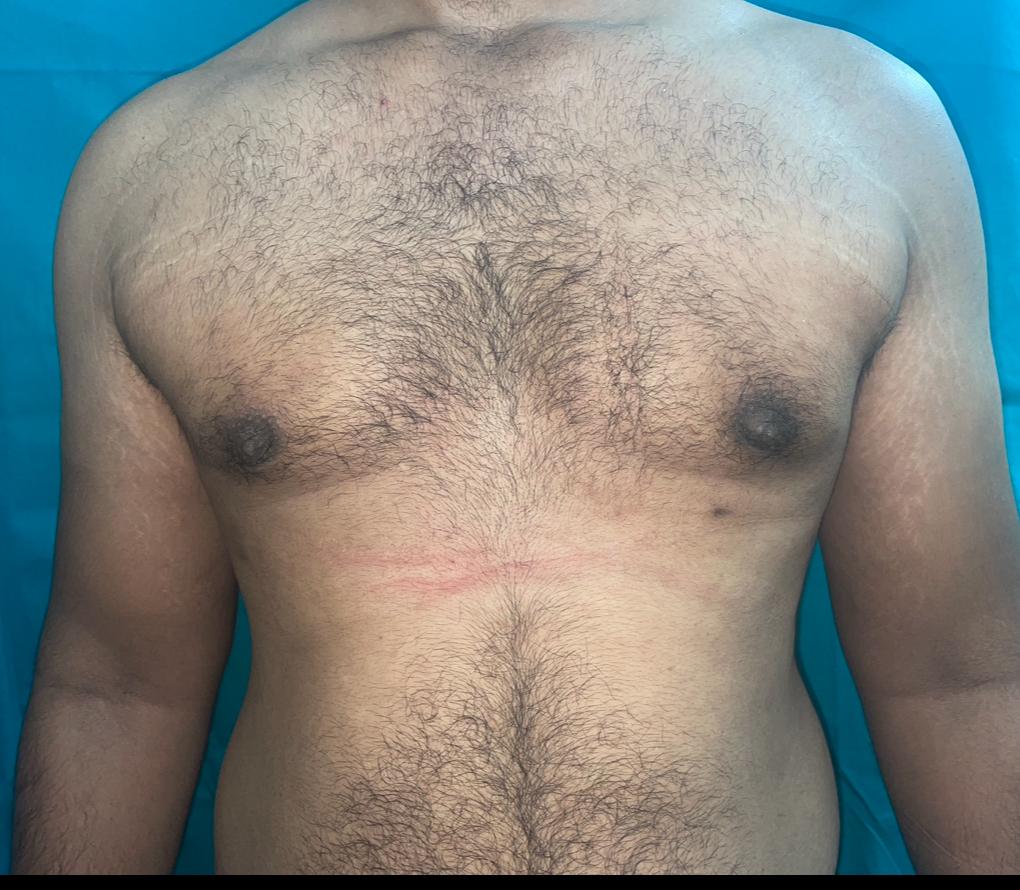
Gynecomastia is the benign enlargement of breast tissue in males. It can occur at any age and is generally caused by an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone levels. Below are key details about gynecomastia:
Causes
- Hormonal Imbalance:
- Natural life stages: Newborns, adolescence, and older adults may experience transient gynecomastia due to hormone fluctuations.
- Elevated estrogen levels or decreased testosterone levels.
- Medications:
- Anti-androgens (e.g., used for prostate issues).
- Anabolic steroids and androgens.
- Certain antibiotics, antidepressants, and anti-anxiety medications.
- Heart medications like digoxin or calcium channel blockers.
- Medical Conditions:
- Liver disease, kidney failure, or thyroid disorders.
- Tumors affecting hormone production (testicular or adrenal).
- Substance Use:
- Alcohol.
- Recreational drugs (e.g., marijuana, amphetamines).
- Obesity:
- Increased body fat can lead to higher estrogen levels, contributing to breast tissue growth.
Symptoms
- Swelling of breast gland tissue.
- Breast tenderness.
- Sometimes pain or sensitivity in the affected area.

Diagnosis
- Physical Exam:
- Assessment of breast tissue, abdomen, and genitals.
- Medical History:
- Medication use, substance history, and any related health conditions.
- Imaging Tests:
- Mammography or ultrasound if needed.
- Blood Tests:
- Hormone levels and liver, kidney, or thyroid function tests.
Treatment
- Observation:
- If the condition is mild or due to temporary hormonal changes, it may resolve without treatment.
- Medications:
- Tamoxifen or raloxifene (off-label use) to address hormonal imbalance.
- Aromatase inhibitors in specific cases.
- Surgical Options:
- Liposuction: Removes excess fat.
- Mastectomy: Removes glandular tissue.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Weight loss and management.
- Avoiding triggers like alcohol or recreational drugs.
Prevention
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid medications or substances known to cause gynecomastia.
- Regular check-ups to monitor underlying health conditions.
If you suspect gynecomastia, consult a healthcare provider USHA Hospitals for a thorough evaluation to rule out underlying conditions and determine the appropriate treatment.
